-
Kidney: Urine Proteins – Proteinuria
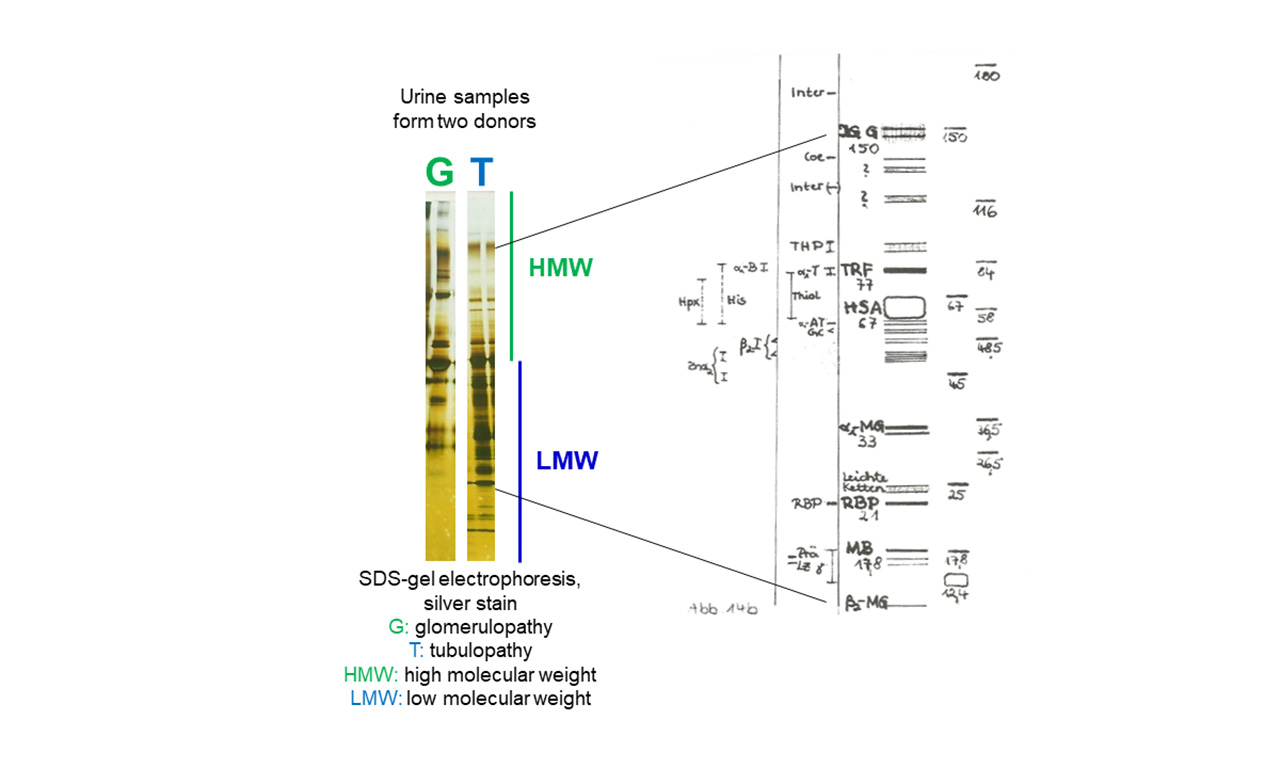
Differentiation between Glomerular and Tubular Nephropathies Proteinuria means an elevated amount of proteins that are excreted within the urine. An early differentiation between high and low molecular weight urine proteins is important for diagnosis and therapy. High molecular weight proteins appear in the urine when glomeruli in the kidney are not functioning properly. Low molecular…
-
Blood-Brain Barrier: CSF Proteins
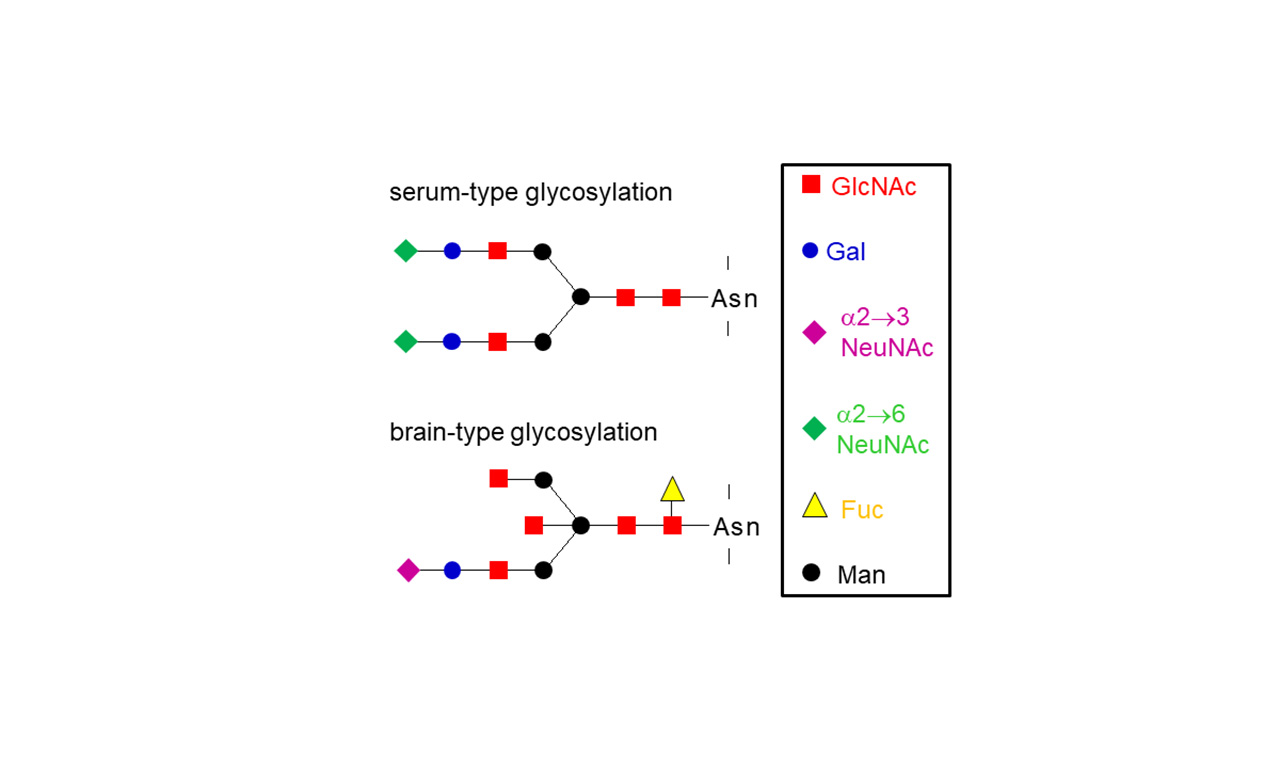
Maintenance of Brain Homeostasis by Sugar Structures CSF – cerebrospinal fluid, in German also called ‘liquor cerebrospinalis’ or ‘Nervenwasser’ – with a particular protein called ‘beta-trace protein’, was the topic of my doctoral thesis ‘Isolation and chemical characterization of -trace protein from human cerebrospinal fluid: identification as prostaglandin D synthase’ (1992) in the CSF laboratory of the Neurological Clinic, MHH. CSF and the…
-
Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy
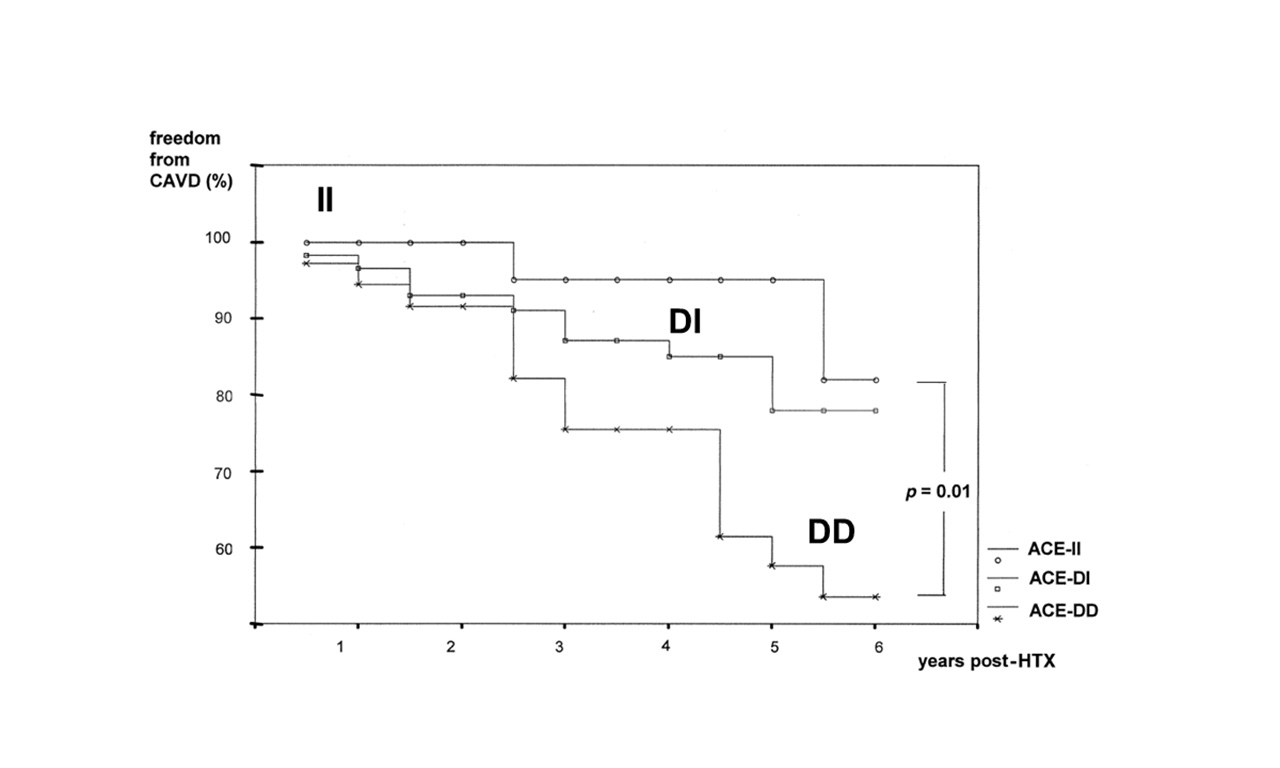
Gene Polymorphisms as Risk Factors In transplanted hearts (also called ̒cardiac allograftsʼ) blood vessels may clog after transplantation. This is called vasculopathy and leads to rejection of the graft. Consequently, for long-time survival of transplanted hearts a strict control of the organ function is mandatory.Patients may have genetic predispositions for upcoming rejection. My work interrogated…
-
Musculoskeletal System: The Intracellular Protein TAK1
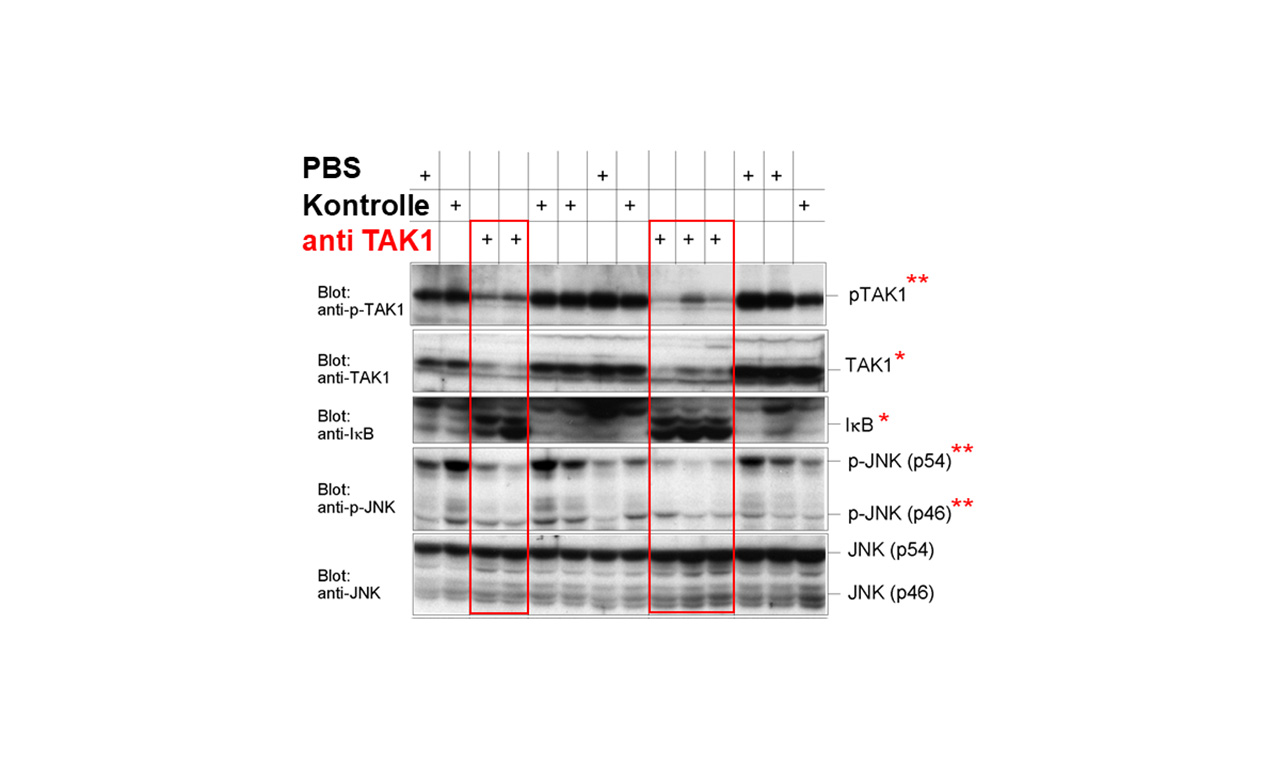
Cell Signaling in Inflammation and Fibrosis TAK1 (transforming growth factor-activated kinase 1) is important for differentiation and regeneration as well as during infections and inflammatory responses. In an inflammatory model of arthritis, we investigated the hypothesis whether silencing of TAK1 would reduce the extent of inflammation and halt subsequent tissue destruction. Injection of lipoplexes with…
